纳米颗粒在离开肿瘤血管进入肿瘤微环境后的行为仍缺乏实验研究。Michael’s Hospital的Devika Chithrani等人利用多细胞层模型研究了金纳米颗粒在组织类型结构内的吸收和分布动力学。结果表面,纳米颗粒的吸收和传输依赖于肿瘤细胞的类型:与MCF-7细胞相比,金纳米颗粒在MDA-MB-231细胞内的穿透距离更深。利用CytoViva成像法对金纳米颗粒在细胞内、外的分布进行了成像分析。多细胞层模型能有效地实现对肿瘤组织的模拟,使其成为实体肿瘤中颗粒分布功效评估的有力工具。
撰写的综述发表于Nano-Micro Letters上2015年第7卷第2期.
全文链接:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40820-014-0025-1
文章引用信息:
Darren Yohan • Charmainne Cruje • Xiaofeng Lu • Devika Chithrani,Elucidating the Uptake and Distribution of Nanoparticles in Solid Tumors via a Multilayered Cell Culture Model,Nano-Micro Lett.(2015) 7(2):127–137, http://dx.doi:10.1007/s40820-014-0025-1
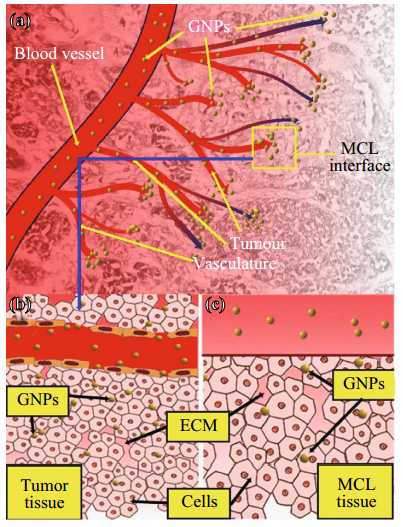
Fig. 1 Use of MCL cell model to understand the NP transport through the tumor tissue. (a) Transport of GNPs through the blood vessels and enters tumor vasculature. The interface between tumor vasculature and tumor tissue is highlighted with a yellow box. (b) GNPs escape the tumor vasculature through leaky endothelial cells (1) and enter tumor cells through ECM. c Description shown in B is modeled using proposed MCL cell model. MCL act as a tumor tissue being fed by tissue culture media containing GNPs (2). (Color figure online)
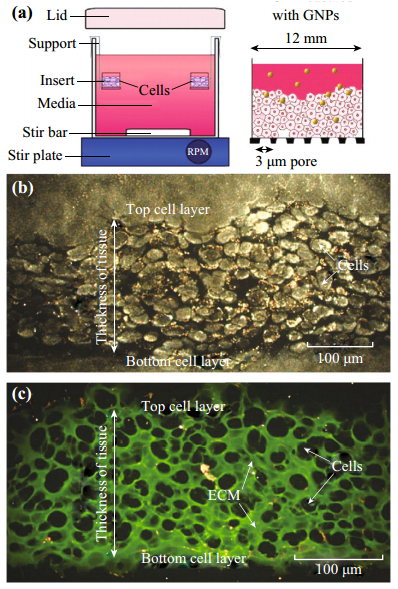
Fig. 2 Growth of MCLs. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the apparatus used to culture MCLs. Tissue culture inserts are held suspended in stirred media (top left). The set-up was placed in a humidified incubator with 5 % O2, 5 % CO2, and 95 % N2. After the growth, GNPs were introduced into the media to investigate the NP transport through tissue (top right). (b) A cross-section of an unstained MCF-7 tissue. c A cross-section of a MCF-7 tissue stained with eosin to map the ECM. Areas marked in green belong to ECM, while the unstained regions represent cells. (Color figure online)
如果文章对您有帮助,可以与别人分享!:Nano-Micro Letters » 利用多层细胞培养模型揭示纳米颗粒在实体肿瘤中的吸收和分布
 Nano-Micro Letters
Nano-Micro Letters NML文章集锦 | 肿瘤靶向治疗
NML文章集锦 | 肿瘤靶向治疗 肿瘤化疗耐药性的”克星”:基因与小分子联动治疗新策略
肿瘤化疗耐药性的”克星”:基因与小分子联动治疗新策略 综述:基于金纳米颗粒的光响应脂质体给药系统
综述:基于金纳米颗粒的光响应脂质体给药系统 东南大学滕皋军院士、芮云峰、王乾乾教授等综述:肌肉骨骼系统中的微机器人
东南大学滕皋军院士、芮云峰、王乾乾教授等综述:肌肉骨骼系统中的微机器人